How Many Excused Absences are Allowed in a School Year
Attendance is the first step in every student’s success.
You can’t learn if you don’t show up.
Understanding attendance policies, including the number of excused absences allowed and the age of required school attendance by state, is crucial for parents and educators. By maintaining a consistent attendance record, students gain not only knowledge but also essential skills such as punctuality, responsibility, and perseverance, which set them up for lifelong success.
We explain the complexities of school attendance policy in the US, shedding light on state-specific guidelines, the importance of regular attendance, and actionable strategies to encourage a student to prioritize attendance.
Key Insights
Excused Absences Vary by State: Each state has specific policies on the number of excused absences allowed, often ranging from 5 to 10 days per year for valid reasons such as illness, bereavement, or legal obligations.
Chronic Absenteeism: Missing 10% or more of the school year, including excused and unexcused absences, is considered chronic absenteeism and can severely impact a student’s academic performance.
Age of Required Attendance: State laws dictate the ages during which children must attend school, with most states mandating attendance between ages 6 and 18, although exceptions apply.
Impact on Academic Success: Regular attendance ensures students build on cumulative lessons, maintain social connections, and receive personalized support from teachers.
Barriers and Equity: Transportation, health challenges, and socioeconomic factors often contribute to absenteeism, highlighting the importance of community and school support to close opportunity gaps.
Why Student Attendance Matters
Student attendance is the foundation of academic success, personal growth, and future opportunities. Consistent attendance ensures students build on cumulative lessons, develop critical social skills, and form strong connections with teachers, all of which are essential for learning and emotional well-being. Regular attendance also prepares students for the workforce by fostering habits like punctuality and reliability while reducing the risk of long-term consequences such as lower earning potential and risky behaviors. For underserved communities, addressing barriers to attendance—like transportation and food insecurity—helps close opportunity gaps, ensuring equitable access to education. Prioritizing attendance is a collective responsibility that empowers students to reach their full potential and contributes to a more equitable and successful society.
How Many Excused Absences are Allowed in a School Year
The number of school days a student can miss before facing consequences varies by state, as each state establishes its own attendance policies and definitions of truancy and chronic absenteeism. For instance, in Maryland, a student is considered truant if unlawfully absent for more than 8 days in any quarter, 15 days in any semester, or 20 days in a school year.
In Ohio, habitual truancy is defined as 30 or more consecutive hours, 42 or more hours in one school month, or 72 or more hours in a school year without a legitimate excuse.
These thresholds are set to ensure consistent attendance, as excessive absences can significantly impact a student's academic performance and overall educational experience. It's important for parents and students to be aware of their state's specific attendance laws to avoid potential penalties and to support academic success.
The number of excused absences allowed in a school year typically varies by state and school district, as policies are set at the local or state level. Common factors influencing excused absences include:
Valid Reasons for Excused Absences:
Illness or medical appointments (doctor’s note may be required).
Family emergencies or bereavement.
Religious holidays.
Legal obligations (e.g., court appearances).
Approved educational opportunities (e.g., college visits).
General Allowances:
Many states or districts allow around 5–10 excused absences per year for reasons like illness or emergencies, though some states permit more with proper documentation.Chronic Absenteeism Threshold:
Chronic absenteeism, often defined as missing 10% or more of the school year (typically 18 days), includes both excused and unexcused absences.
For a more precise number of allowed excused absences, it’s best to consult specific state laws or local school district policies, as the rules can differ significantly.
How to Encourage a Student to Attend School
Encouraging a student to prioritize school attendance involves a mix of creating a supportive environment, addressing barriers, and fostering motivation. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Foster a Positive School Experience
Make Learning Exciting: Highlight the enjoyable aspects of school, such as favorite subjects, extracurricular activities, and friendships.
Build Relationships: Encourage connections with teachers and peers to create a sense of belonging.
Celebrate Milestones: Recognize achievements, like a good attendance record, to motivate continued commitment.
2. Communicate the Importance of Attendance
Explain Long-Term Benefits: Discuss how consistent attendance leads to better grades, higher graduation rates, and future opportunities.
Emphasize Responsibility: Teach students how habits like punctuality and consistency prepare them for college and careers.
3. Create a Routine at Home
Establish Morning Habits: Set clear bedtime and morning routines to reduce stress and tardiness.
Set Priorities: Ensure school is treated as a non-negotiable part of daily life.
4. Address Barriers to Attendance
Identify Issues: Talk openly with the student to understand any problems, such as bullying, transportation challenges, or health concerns.
Seek Solutions: Work with the school to provide resources like counseling, tutoring, or flexible learning options.
5. Involve Parents and Educators
Parent Engagement: Parents can monitor attendance, communicate with teachers, and create a supportive home environment.
Educator Support: Teachers can create engaging lessons, build trust, and intervene early when absenteeism is detected.
6. Use Rewards and Recognition
Incentives: Offer small rewards for consistent attendance, such as certificates, outings, or privileges.
Positive Reinforcement: Acknowledge improvements and effort to build confidence and enthusiasm.
7. Teach the Value of Commitment
Role Models: Share stories of successful individuals who benefited from prioritizing education.
Goal Setting: Help students set academic and personal goals, showing how attendance contributes to achieving them.
By combining these approaches, parents and educators can instill the importance of regular attendance and help students develop a lifelong commitment to their education.
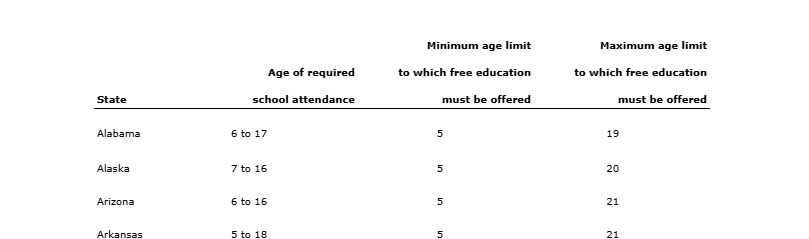
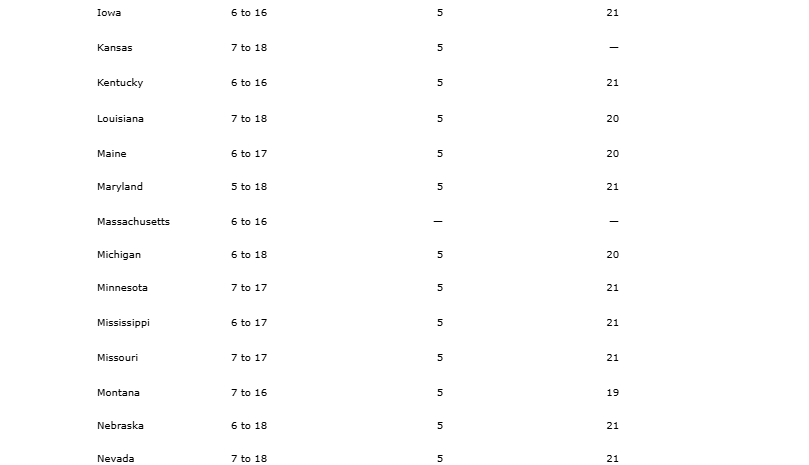
Age of Required School Attendance by State
State laws define the age range during which children are required to attend school, often starting at 5 to 7 years old and extending to 16 to 18 years old. For example, in California, attendance is mandatory from ages 6 to 18, while in Maryland, the range is 5 to 18. Some states, like Texas, extend the maximum age to 19, ensuring access to education for older students. This variation underscores the importance of understanding state-specific requirements to ensure compliance and support for student success.
Source: National Center fro Education Statistics
The Bottom Line
Attendance plays a pivotal role in shaping a student’s academic and personal success. State-specific policies on excused absences and required attendance ages reflect the importance of consistent school participation. Whether through fostering parent engagement, addressing systemic barriers, or leveraging state resources, improving attendance is a collective responsibility. By prioritizing attendance, we can ensure every child has the opportunity to reach their full potential, contributing to a more equitable and prosperous society.
FAQs
How many excused absences are typically allowed in a school year?
The number of excused absences varies by state and district, but most allow 5 to 10 days per year for valid reasons such as illness, bereavement, or religious holidays.
What is chronic absenteeism?
Chronic absenteeism is defined as missing 10% or more of the school year, including both excused and unexcused absences, which can significantly affect a student’s academic performance.
At what age does school attendance become mandatory?
Mandatory attendance generally begins between ages 5 and 7, depending on the state, and typically continues until 16 or 18. For example, California requires attendance from ages 6 to 18, while Florida mandates attendance from 6 to 16.
What are valid reasons for excused absences?
Valid reasons often include illness, family emergencies, religious observances, legal obligations, or approved educational opportunities such as college visits.
How can schools support consistent attendance?
Schools can implement reward systems, provide flexible learning options, address bullying or mental health concerns, and collaborate with communities to remove barriers like transportation and food insecurity.